Blood clots are dangerous and often silent. They block blood flow in vessels. This can lead to serious health problems. A clot in the heart may cause a heart attack. A clot in the brain may lead to a stroke. Both are life-threatening conditions. Doctors prescribe blood thinners to stop this. These medicines prevent new clots from forming. They save lives every day. But many people have one key question: what are the top 10 blood thinners? This question matters because patients want to know which drugs are trusted and most effective.
Families also want to learn about their role in protecting health. In this guide, we will explain in detail. You will learn what blood thinners are. You will see why they are needed. And also will also know the two main types. And finally, you will discover the top 10 medicines in detail.
What Is a Blood Thinner?
A blood thinner is a medicine that prevents dangerous clots. It does not literally make the blood thinner. Instead, it changes the clotting process inside the body. Some drugs prevent platelets from clumping together. Platelets are small blood cells that start clotting. Other drugs block proteins called clotting factors. These proteins are important for normal wound healing. But in excess, they cause harmful clots inside blood vessels.
So, blood thinners protect against blocked vessels. They keep blood flowing smoothly. They lower the risk of stroke, heart attack, and other clot-related conditions. When people ask what are the top 10 blood thinners, they are asking which drugs are most effective at this task. Knowing them helps patients understand their treatment better.
Why Do People Need Blood Thinners?
Blood clots can form at any time. They may form in legs, arms, lungs, or brain. They may form after injury, surgery, or even without any reason. These clots can travel through the bloodstream and block vital organs.
Doctors prescribe blood thinners to stop this process. Some patients need them after a heart attack. Some need them after stent placement. Others may require them due to atrial fibrillation, a heart rhythm disorder that increases stroke risk.
Without blood thinners, patients may suffer repeated clots. With proper use, their risks drop sharply. That is why asking blood thinners is an important step for anyone at risk.
The Two Main Types of Blood Thinners
Doctors classify blood thinners into two groups. Each group has a different role. Both are important for protecting health.
1. Antiplatelet Drugs
Antiplatelets target platelets, the small cells that help start clotting. They prevent platelets from sticking together. By doing this, they stop small clots from growing inside blood vessels. They are usually prescribed to heart patients. These drugs are commonly given after bypass surgery, stent placement, or a heart attack. They lower the risk of repeat events.
2. Anticoagulant Drugs
Anticoagulants work on clotting factors, which are proteins in blood. They block these proteins from forming clots. This makes them stronger than antiplatelets. They are prescribed to patients with deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, or atrial fibrillation. They are also used in high-risk surgical cases. Both groups are needed in medicine today. And both groups include drugs that appear in the list of what are the top 10 blood thinners.
What are the Top 10 Blood Thinners?
Here is a detailed list. Each drug is explained clearly for easy understanding.
1. Aspirin
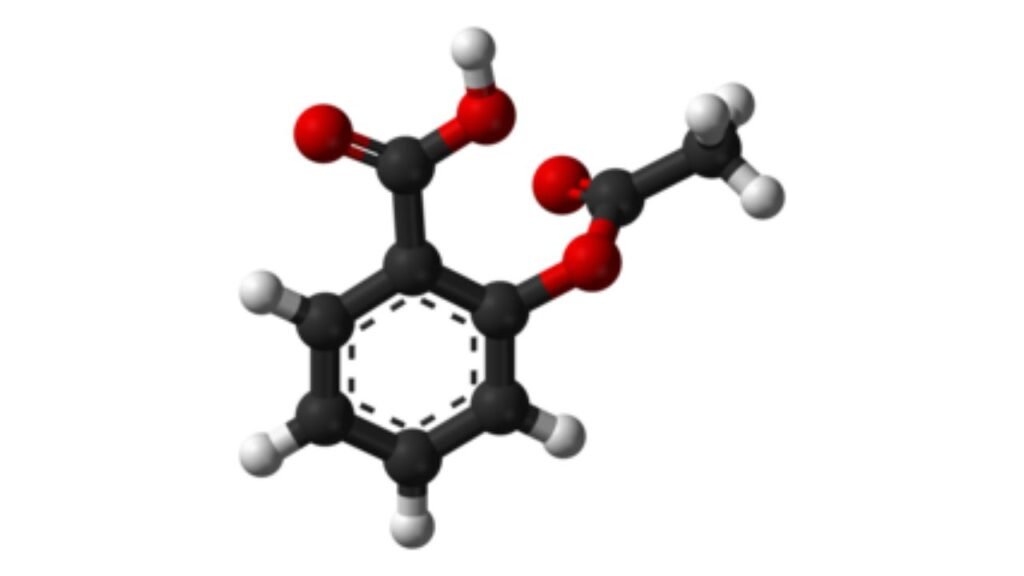
Aspirin is the most common blood thinner worldwide. It is cheap and available everywhere. It works by stopping platelets from sticking together. Doctors prescribe it for patients with heart disease, stroke history, or bypass surgery. It is often used long-term. A small daily dose can protect against heart attacks. It is also combined with other drugs for stronger protection.
2. Clopidogrel (Plavix)
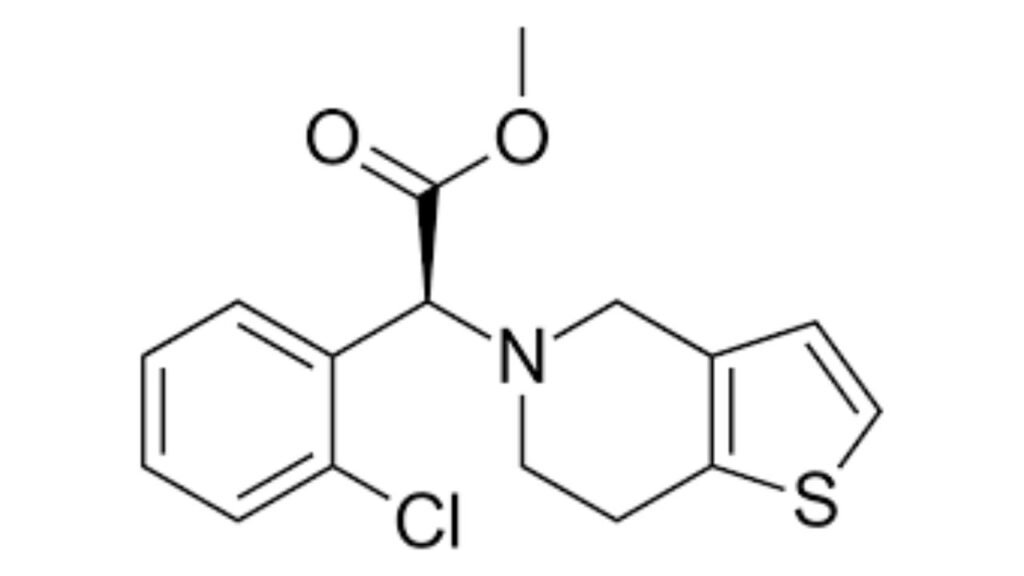
Clopidogrel is an antiplatelet drug. It is stronger than aspirin. It is often prescribed after stent placement and prevents the stent from getting blocked by clots. Doctors also use it for patients who cannot tolerate aspirin. It reduces stroke risk and improves survival in heart patients.
3. Ticagrelor (Brilinta)
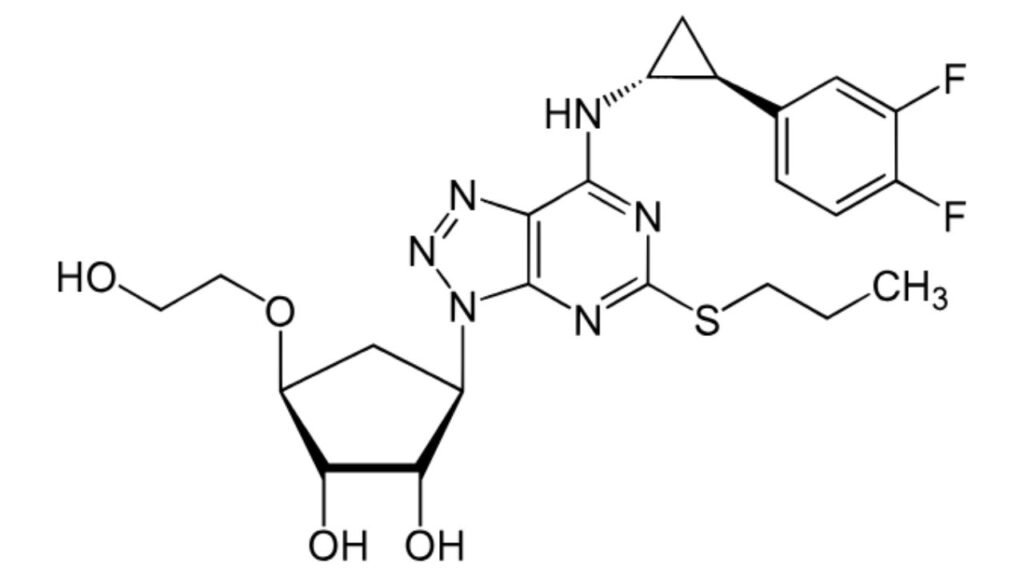
Ticagrelor is a powerful antiplatelet drug. It works faster than clopidogrel. Doctors often use it in acute coronary syndrome. It lowers the chance of another heart attack. It is usually taken daily under medical advice. Ticagrelor is one of the top modern choices when people ask what are the top 10 blood thinners.
4. Prasugrel (Effient)
Prasugrel is another strong antiplatelet drug. It is used in combination with aspirin. Doctors use it after heart surgeries or stent placement. It reduces the chance of clot formation in arteries. But it carries a slightly higher bleeding risk. This is why it is prescribed with caution.
5. Dipyridamole (Persantine)
Dipyridamole works in a unique way. It raises chemical levels in blood that stop clotting. It is often combined with aspirin for stroke prevention. Doctors prescribe it for patients with a history of stroke or mini-stroke. It is usually part of long-term therapy.
6. Warfarin (Coumadin)
Warfarin is one of the oldest anticoagulants. It blocks vitamin K, which is needed for clotting proteins. It has been used for decades. Patients taking warfarin need regular blood tests. This ensures the drug is working correctly. It is mainly prescribed for atrial fibrillation or deep vein thrombosis.
7. Heparin
Heparin is a fast-acting anticoagulant. It is usually given by injection in hospitals. It prevents clots during surgery or in emergency cases. Doctors use it for patients with active clot risks. It is not usually prescribed for home use.
8. Enoxaparin (Lovenox)
Enoxaparin is a type of low-molecular-weight heparin. It is more stable than normal heparin. It is given by injection. Doctors prescribe it for deep vein thrombosis prevention. It is also used after surgeries to lower clot risks.
9. Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
Rivaroxaban is a modern anticoagulant. It belongs to a class called DOACs. Rivaroxaban blocks clotting factor Xa. It is prescribed for stroke prevention, pulmonary embolism, and deep vein thrombosis. Unlike warfarin, it does not require regular blood testing.
10. Apixaban (Eliquis)
Apixaban is another modern DOAC. It blocks factor Xa like rivaroxaban. But it is considered safer for long-term use. It has a lower risk of bleeding compared to older drugs. Doctors often prefer it for atrial fibrillation patients.
Safety Tips While Using Blood Thinners
Using blood thinners requires care. Patients must follow strict rules. These prevent complications and bleeding risks.
- Avoid alcohol in large amounts.
- Inform doctors before surgery or dental work.
- Do not stop medicines suddenly.
- Be careful with sharp objects.
- Keep a steady diet, especially with warfarin.
Conclusion
So finally, The top list includes aspirin, clopidogrel, ticagrelor, prasugrel, dipyridamole, warfarin, heparin, enoxaparin, rivaroxaban, and apixaban. These are the most trusted drugs used worldwide.
Each medicine has a specific role. Some protect against heart attacks. Others prevent strokes. Some are used in hospitals, while others are taken long-term at home.
Blood thinners save countless lives. They prevent dangerous clots. But they also carry risks like bleeding. This is why medical supervision is necessary. Knowing what are the top 10 blood thinners builds awareness. It helps patients understand their treatment. And it ensures safer health choices for the future.
People Also Ask
Q1. Do blood thinners cure existing clots?
No, They prevent new clots. Old clots may need other treatments.
Q2. Can I travel while taking blood thinners?
Yes, Keep medicines with you. Stay active during long journeys.
Q3. Which blood thinner is safest?
Newer DOACs like apixaban are safer. They have fewer bleeding risks.
Q4. Can food affect blood thinners?
Yes, Vitamin K foods affect warfarin. Keep diet steady for safety.
Q5. Do I need tests while on blood thinners?
Older drugs like warfarin require tests. Newer DOACs often do not.
Read Our More Blogs: Carrot Juice Benefits: Health, Skin, Eyes & Heart Care